Efficacy and Safety of Tofacitinib as Monotherapy in Japanese Patients With Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: A 12-Week, Randomized, Phase 2 Study
Mod Rheumatol. 2014 Dec 11:1–25. [Epub ahead of print]
The oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib has demonstrated efficacy as monotherapy or in combination with DMARDs for the treatment of active RA in Phase 3 randomized controlled trials in various patient populations. As such, this phase 2 study aimed to evaluate multiple doses of tofacitinib monotherapy vs placebo for the treatment of RA in Japanese patients who have had an inadequate response to synthetic or biologic DMARDs.
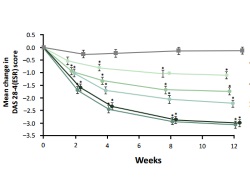
Tofacitinib demonstrated dose-related efficacy versus placebo by statistically significantly greater rates of patients achieving ACR20. Additional significant improvements were seen in secondary measures such as changes from baseline in DAS28-4(ESR). The safety profile was consistent with that seen in global monotherapy trials and other studies in Japanese patients.